

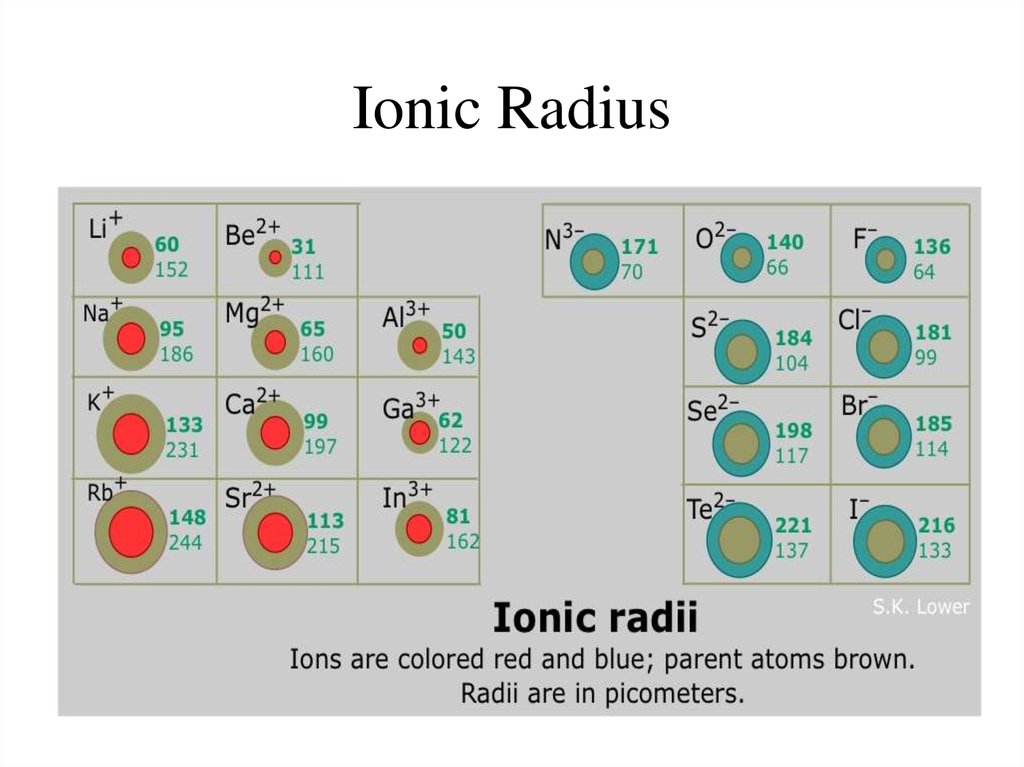
(ix) The elements at the extreme left of the periodic table are metals. (viii) In a group, the Ionization energy decreases with increasing atomic number from top to bottom. For alkali metals it has the lowest value in a period and for a noble gas it is the largest in the period. Ionisation energy increases from left to right in a period. (vii) Ionisation energy is the energy needed for the removal of an electron from a gaseous isolated atom to form a gaseous cation. This is due to decrease in the effective nuclear charge. The radius of an anion is greater than the radius of the atom from which it is formed.
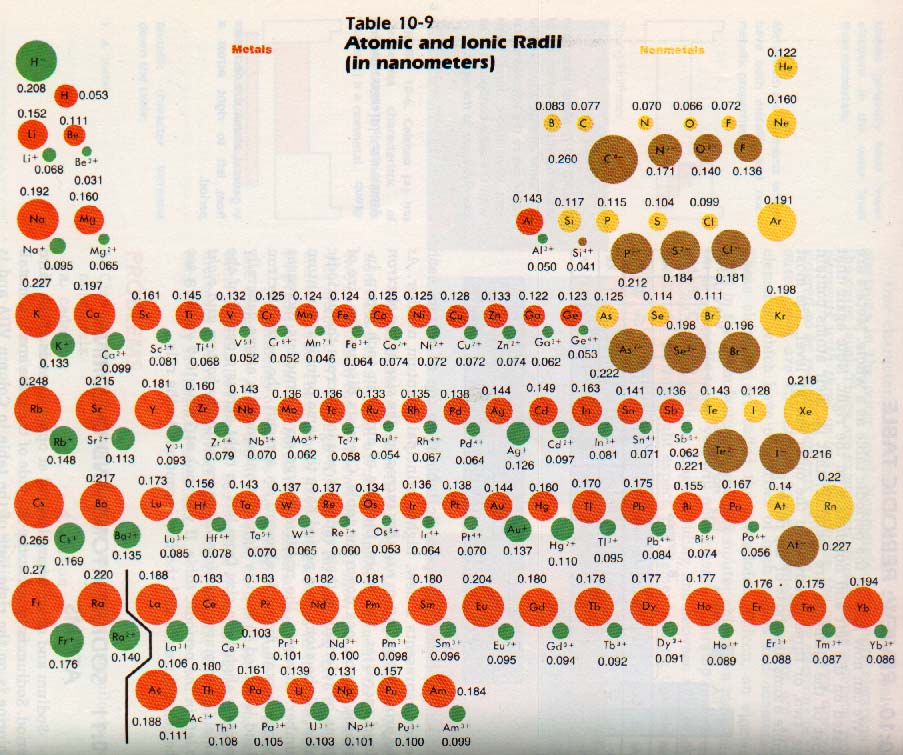
This is due to increase in effective nuclear charge. But the atomic radius of a noble gas is largest in the period 18.The radius of a cation is smaller than the radius of the atom from which it is formed. (vi) In a period, the atomic radii decrease with increasing atomic number from left to right. (v) In a group the atomic radii increase with increasing atomic number from top to bottom. (iv) Each element of a group has the same valency which is a characteristic of that group.
(iii) n a period, the valency of elements varies from 1 - 4, then decreases from 4 - 1 and becomes zero for noble gases. (ii) In a group the number of valence electrons does not change on moving from top to bottom. (i) In a period, the number of valence electrons increases on moving from left to right. This is done to save space and to have the elements with similar chemical properties at a single place.ĥ. (vii) Lanthanides and actinides are placed in two separate rows at the bottom of the periodic table. They are positioned between s-and p-block elements of the periodic table. (vi) d-block elements are called transition elements. (v) Elements of group 13, group 14, group 15, group 16, group 17 and group 18 collectively constitute p-block elements.

These are placed in group 1 of the periodic table s-block elements with 2 valence electrons are called alkaline earth metals. (iv) s-block elements with 1 valence electron are called alkali metals. (iii) s-and p-block elements are called representative elements. These are called s-block elements, p-block elements, d-block elements and f-block elements. (ii) On the basis of similarities and dissimilarities in the electronic configurations all the known elements have been classified into blocks. (i) Modern periodic table is divided into 7 horizontal rows called periods and 18 vertical columns called groups. This law states that properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.Ĥ. Modern periodic table: Long form of periodic table Modern periodic law is based on the atomic numbers and electronic configurations of elements. He proposed the periodic law that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic masses. (ii) Mendeleev classified the elements into groups and periods. (i) Dobereiner, Newlands and Mendeleev proposed the classification of elements on the basis of their chemical properties and atomic masses (atomic weight). Early attempts of classification of elements The classification of elements is required for a convenient and systematic study of the behaviour and nature of substances.Ģ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
